 By Owen
By Owen  2018-04-24
2018-04-24 laser die cutter,
laser die cutting,
laser rotary die,
laser flat die,
laser die cutter,
laser die cutting,
laser rotary die,
laser flat die,
How does laser die cutting work?
In this blog, we will describe all the processes needed to come to a perfect result.
We need to deepen laser die cutting into two major aspects:
1) laser flat die by flat die making machine
2) laser rotary die by rotary die making machine
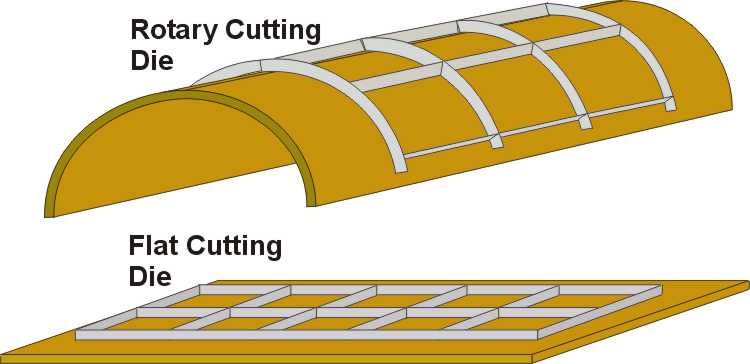
Flat die by laser die cutter
The flat die is made of birch wood and usually has a thickness of 18 mm. Panels must adhere to tolerances in terms of thickness and flatness, otherwise large problems can occur during laser die cutting.
Laser die cutting is performed in accordance with strict guidelines relating to the width of the laser die cutting channel, with an accuracy of 0.71 mm (2 points) or 1.07 mm (3 points).
The latest generation of laser die cutter, with software, can modulate 8 directions of cutting with precise offsets. The precision cutting die must have the same precision width in the upper and lower parts to ensure the tightness of the cutting line.
There are many factors that affect the precision of the laser die by laser die cutter, such as machine characteristics (using a high-precision recirculating ball screw or a linear motor), and the focus accuracy and stability of the laser flow.
In addition to laser cutting, current marker heads are often used to write a large amount of information
Stamping is completed in seconds, saving time and gas.
Rotary die by laser die cutter
Laser rotary dies are usually obtained from 13mm poplar wood with diameters from 176mm to 800mm.
In the case of flat die, rigid rules that obey certain flatness and thickness are the most basic, even if the die is rotated. The cut usually has a width of 1.42 mm (4 points).
The laser rotary die cutting begins with off-line assembly of the exterior of the machine by screwing the wooden support into the lower cavity of the rotating housing and then housing it in the rotating housing.
The laser die cutter head is then equipped with a tool changer so that special pockets can be milled, which is essential for assembling additional supports for laser rotary die cutting.